
Therefore, accurate gravity can be measured everywhere depending on the global Bouguer gravity anomaly ( Figure 1). (13) requires the formulation of the overall Bouguer effect as a function of the density of the rock ( ρ = 2.65 g/cm 3) and the height ( h) denoted as 0.04193 ρh. Moreover, the effect of the Bouguer anomaly in Eq. (13) involving free-air correction presents the gravity changes due to the height of the ellipsoidal Earth, 0.3086 h. Since the Earth is spherical, the gravity is calculated using Eq. In the following section, details of the HIGF equation are explained. The main novelty of this study is the formulation of four coefficients gravity formula based on the gravity measurement above sea level. The gravity at different elevations and latitudes can be measured using the HIGF and compared with the modified IGF84 (WGS84). This experimental gravity equation was introduced in the form of the Hezar International Gravitational Formula (HIGF). In the present study, we introduced a new four-coefficient gravimetric formula where the coefficients are calculated using experimental gravity data from four-point sets around the world. Therefore, the Hezar summit unexpectedly has a low gravity value throughout Iran. According to the physical geodetic survey performed at the National Cartographic Center of Iran (NCC), the gravity of summit Hezar is 203 mGa l lower than that of Mount Damavand’s peak. The study revealed that the WGS84 model cannot explain the experimental gravity of the summits and the Earth’s surface, including the difference of −203 mGal in gravity between the peaks of the Hezar and Damavand mountains (4,499.416 m and 5,605.730 m, respectively). Therefore, this study focuses on the formulation of an experimental model to estimate Earth’s gravity. Īlmost all of the above mentioned models are theoretical models to estimate Earth’s gravity. Of which, the WGS84 equation was modified by several scholars. The two Earth Gravitational Models (EGM) that are the best models to calculate gravity include EGM96 and EGM2008, while the best-known IGFs are GRS30, GRS1967, GRS80 and WGS84. Hence, the new formulation of gravity required the computation of normal gravity at different points.

Moreover, various systematic errors in computing the normal gravity were observed at the topographical surface on the Earth. The IGF does not explicitly depend on the Earth’s flattening because it is a theoretical gravity model. The differences between the 1930 IGF and GRS 67 were discussed by Lysonski. The GRS 67 was compatible with the International Gravity Standardisation Net 1971 datum. However, the 1930 IGF was further modified in 1967 by Geodetic Reference System (GRS 67), which was then refined and described by Woollard in 1979 using accurate satellite data by Jacobs in 1974. The 1930 IGF also incorporated the Potsdam datum. The 1930 IGF was based on Clairaut’s model, which was first developed in 1777. In 1930, the International Gravity Formula (IGF) was adopted to calculate the theoretical value of gravity at any point on the spheroid. The Earth is spheroidal and its surface is spheroid. The results indicated that the experimental HIGF as g =978,031.85 ( 1 + 0.0053024 sin 2 θ−0.000032309786 sin 2 2θ) −0.27 h was in agreement with the practical gravity compared to the 1984 International Gravitational Formula (IGF84). Apart from describing the 213 mGal difference in gravity between Hezar summit and peak of Mount Damavand, HIGF is also in agreement with practical gravity with distance from sea level and latitude (93% confidence level). This study attempts to modify the conventional version of Hezar International Gravity Formula (HIGF) to calculate the experimental gravity in the Earth’s summits and land surfaces. Recently, the exact value of gravity at the Hezar summit and peak of Damavand mount have been measured.
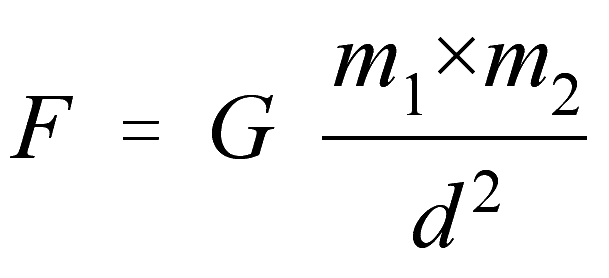
The gravity recorded at the Hezar summit (4,499.416 m) was 213 mGal (0.00213 m/s 2) lower than the reading recorded at the peak of Mount Damavand (5,605.730 m). The National Cartographic Center of Iran measured the differences in gravity between the Hezar summit and peak of Mount Damavand using a CG-5 gravity meter. 4Centre for Applied Physics and Radiation Technologies, School of Engineering and Technology, Sunway University, Subang Jaya, Malaysia.3Department of Photonics, Faculty of Modern Science and Technology, Graduate University of Advanced Technology, Kerman, Iran.2Department of Nuclear Engineering, Faculty of Modern Sciences and Technologies, Graduate University of Advanced Technology, Kerman, Iran.1Space Science Centre (ANGKASA), Institute of Climate Change (IPI), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi, Malaysia.Mehdi Hassanpour 1*, Mohammad Reza Rezaie 2*, Saeedeh Khezripour 3, Mohammad Rashed Iqbal Faruque 1* and Mayeen Uddin Khandaker 4


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
